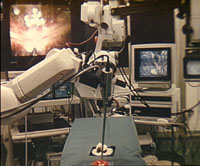

Techniques of telemedicine are still developed further into the direction of interactivity. To enable an external observer to take the initiative and perform certain manipulations in the system an optimal visual perception is a precondition. Keywords to these advances are telemanipulation, telenavigation and telerobotics. The existing mental reservations against the use of robots in medicine are understandable and principally justified. A robot, as known from carindustry, which works down a determined program cannot fulfil the complex and varying demands in medicine. In contrast to this "robotisation" we work on the field of telemanipulation. The physician in this context remains active and in permanent control of his actions. And even further, these activities can be performed at any place of the world alike. This concept necessarily depends on the immediate feedback of evoked results. As a consequence on the one hand highly sensitive instruments have to be designed, which constantly measure changes of the local environment in which they are being used, e.g. the strength of tissue. On the other hand sensitive interfaces are necessary to submit these conditions to the active physician at the remote site.
In our sense of telemanipulation for example in the immediate histological diagnosis during surgery new perspectives are opened by the use of a remote control microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) which is situated directly in the operating room. The integration of locally remote experts for diagnosis and therapy planning (expert consulting) is thus possible.
External Visitors Internal Visitors
These counters were activated on 14.02.03.